Bond Linking Monomers in Polymers
Bond Linking Monomers in Polymers: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Peptide Bond, Glycosidic Bond, Phosphodiester Bond and, Secondary Structure of DNA
Important Questions on Bond Linking Monomers in Polymers
Choose the correct combination for ester bond formation with respect to a polymer of nucelotide.
The Watson-Crick structure of DNA is
The bond present between two nucleotides is
The linkage represented by arrow is
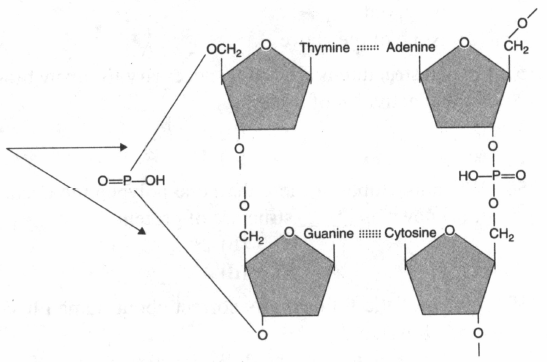
There are adenine and guanine in a stretch of mRNA. How many phosphodiester (A) bonds are there?
The carbohydrate below has been formed from two glucose molecules.
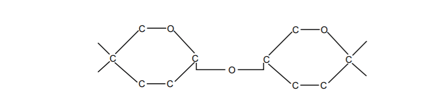
What is the name of the chemical bond which joins these two hexose units together?
Which type of reaction is shown by the following figure
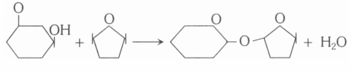
Formation of both peptide and glycosidic bonds involves
Non-proteinaceous enzyme that acts as a catalyst for the formation of peptide bond is _____
"All enzymes are proteins." This statement is now modified because an apparent exception to this biological truth is _____
Many of the hydrolytic reactions are
The type of linkage present in carbohydrates is
Choose the statement 'Is a random coil a secondary structure' as True or False.
The two types of secondary structures are there in protein. One is a Beta-sheet and the other one is an alpha-helix or gamma-helix?
What is the secondary structure of DNA?
What is phosphodiester bond in biology?
During the formation of a peptide bond, the ion is removed from
During the elongation of a polypeptide chain, a new amino acid can be added at
Who performed X-ray diffraction studies of DNA?
A peptide bond is formed by _________ of water molecules between two amino acids.
The bond present between two nucleotides is known as
If the molecular mass of an amino acid is 150 daltons, the molecular mass of a tripeptide will be
